As the Indian GST system moves towards greater digitalisation, the introduction of e‑invoicing has brought new compliance challenges for businesses and tax professionals.
Among the many complexities is understanding and filing for e‑invoice exemption declarations. This guide aims to walk Tax Professionals through the process, ensuring businesses remain compliant while minimising risk.
Whether you're advising clients or handling compliance yourself, this post will provide actionable insights on e‑invoice exemption filing under GST.
Preface to e‑Invoice Mandate and Exemption Declaration Filing
The e‑invoice mandate was introduced under the GST framework to streamline reporting and improve transparency.
Under this mandate, businesses whose aggregate turnover exceeds a specific threshold must generate invoices in a prescribed digital format, submit them to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP), and integrate this data with their GST returns.
For tax pros, one of the most critical tasks is ensuring clients comply with this mandate, or if exempt, file the necessary e‑invoice exemption declaration. With the new compliance requirements, failing to do so can result in severe consequences, including blocked Input Tax Credit (ITC) for buyers, non-compliance penalties, and audit risks.
In this blog, we'll break down the e‑invoice exemption framework for businesses and provide a step-by-step guide to filing exemption declarations accurately, ensuring businesses remain compliant with the latest GST rules.
What is e‑Invoicing, and Who Needs to File an Exemption Declaration?
Understanding the e‑Invoice Mandate
e‑Invoicing, as per the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime, refers to the mandatory reporting of B2B invoices on the IRP by certain businesses.
The primary goal of e‑invoicing is to prevent tax evasion and ensure that the data flows seamlessly between different systems, facilitating faster compliance and reporting.
- Threshold Limits: The e‑invoicing requirement applies to businesses with a turnover above ₹5 crore in the preceding financial year (effective from August 1, 2023). However, even if a business exceeds this threshold, it may still be eligible for an e‑invoice exemption.
- Scope of e‑Invoicing: The e‑invoicing system is applicable for B2B transactions, certain B2G transactions, and other specified transactions like debit/credit notes related to sales.
Who Qualifies for e‑Invoice Exemption?
Certain businesses, regardless of their turnover, are exempt from generating e‑invoices. These include:
- Banks and Financial Institutions: Including non-banking financial companies (NBFCs).
- Government Bodies and Local Authorities: They are not required to comply with the e‑invoice mandate.
- Transporters (Goods Transport Agencies): Specifically for those involved in the transportation of goods by road.
- Passenger Transporters: Including entities providing transportation services for passengers.
- SEZ Units: Special Economic Zones (SEZ) units are not required to generate e‑invoices for their transactions.
In cases where businesses are exempt, they must file an e‑invoice exemption declaration to notify the GST authorities and formalise their exemption status.
Why Filing an Exemption Declaration is Important
Protecting Client Interests
As a tax professional, your role is crucial in ensuring that your clients understand whether they qualify for e‑invoice exemptions and that they properly document their exemption status. Failure to file an exemption declaration could lead to:
- Risk of ITC Denial: Buyers may not be able to claim ITC on invoices that should have been e‑invoices.
- Audit Risks: Non-compliance can attract scrutiny from tax authorities, especially during GST audits or assessments.
- Operational Risks: Incorrect filing or missed exemption declarations may create operational hurdles, particularly during high-volume billing periods.
What Does an Exemption Declaration Do?
By filing an exemption declaration, businesses formally inform the GST authorities of their exempt status under specific provisions, ensuring that their invoices are not flagged for non-compliance. The declaration process is important in preventing disputes or discrepancies during audits.
Step-by-Step Guide to Filing the e‑Invoice Exemption Declaration
Step 1: Verify Eligibility for Exemption
Before proceeding to file an exemption declaration, Tax Professionals must confirm whether the client is eligible for the exemption.
Key steps include:
- Assess Aggregate Turnover: Check if the client’s turnover exceeds the ₹5 crore threshold for mandatory e‑invoicing. This can be verified using the client’s GSTIN and turnover details from previous financial years.
- Review Exemption Criteria: Ensure the client falls under any of the exempt categories, such as banks, financial institutions, government bodies, and others mentioned above.
- Documentation: Gather supporting documentation such as GST registration details, proof of turnover, and relevant exemption notifications.
Step 2: Access the e‑Invoice Portal
Once the eligibility is confirmed, the next step is to file the exemption declaration on the official e‑invoice portal.
- Visit the e‑Invoice Portal: Go to einvoice.gst.gov.in.
- Login: Use the GSTIN credentials to access the portal.
- Navigate to the Exemption Declaration Section: On the dashboard, find the section for e‑invoice exemption declaration filing.
Step 3: Complete the Exemption Declaration Form
Fill in the necessary details in the exemption declaration form:
- Select Exemption Category: From the dropdown, select the appropriate exemption category that applies to your client.
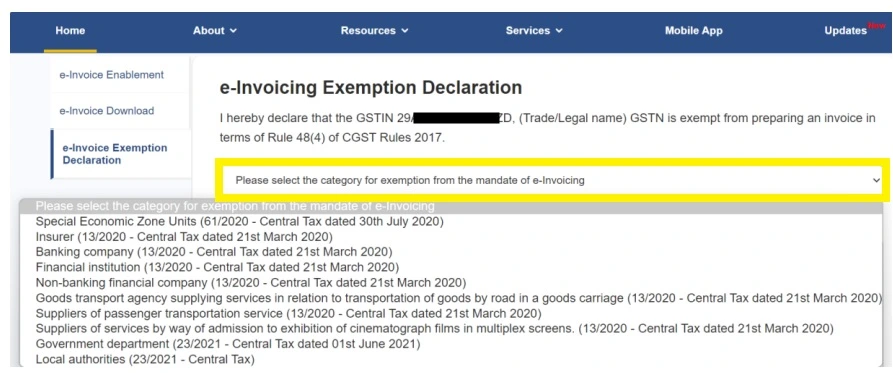
- Declaration Statement: Tick the declaration box to confirm that the client qualifies for the exemption under the relevant rules.
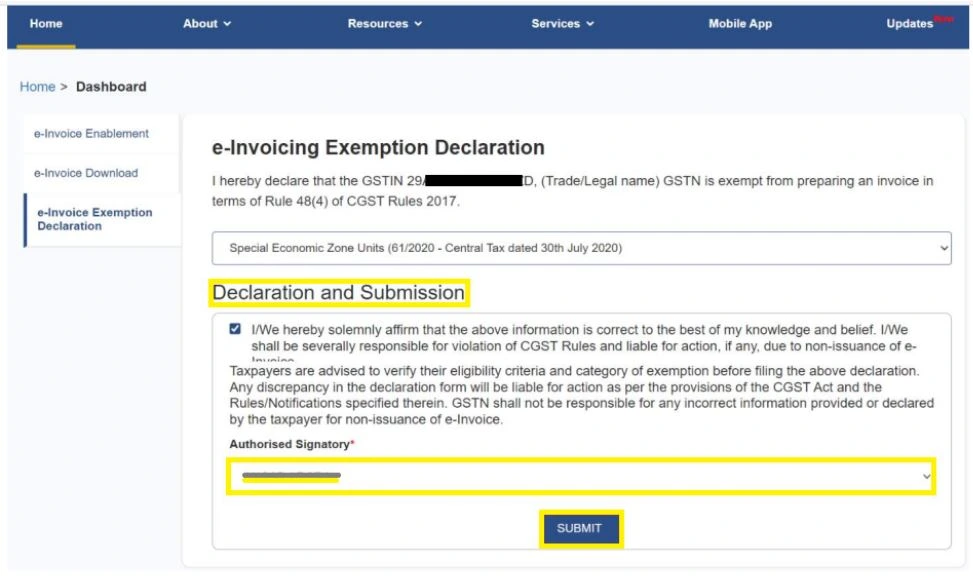
- Authorized Signatory: Ensure that the declaration is signed by an authorized signatory using a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) or Electronic Verification Code (EVC).
- Submit and Acknowledge: Submit the form. Once successfully filed, you will receive an acknowledgment number. Download the PDF acknowledgment for future reference and client records.
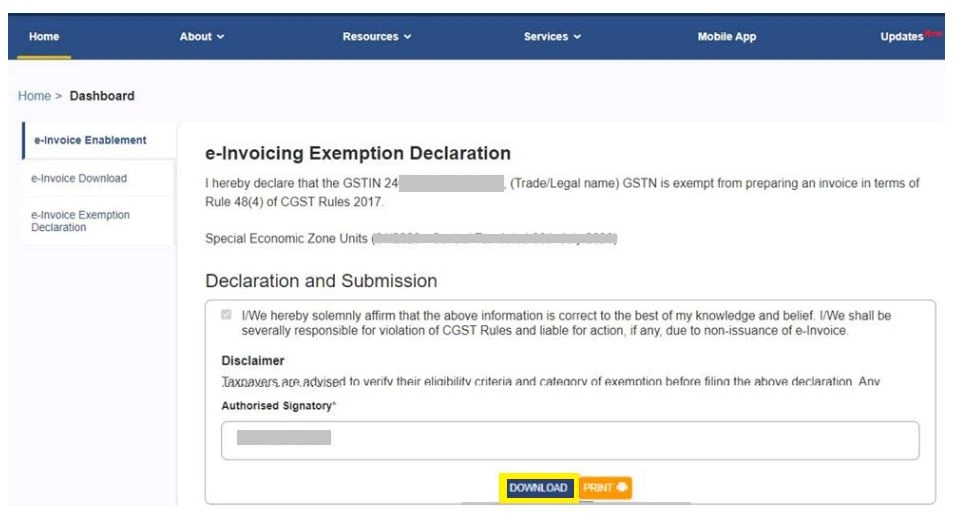
Step 4: Post-Filing Compliance
After filing the exemption declaration, ensure that the client’s invoices reflect the correct exemption status:
- Invoice Footer: For exempt entities, include a declaration on invoices, such as: "We hereby declare that due to our exemption status under Rule 48(4), we are not required to issue an e‑invoice."
- Audit Documentation: Maintain copies of the exemption declaration filing acknowledgment, eligibility assessment, and invoice samples with the exemption footer. These documents will help during GST audits or assessments.
Key Challenges in e‑Invoice Exemption Filing and How to Overcome Them
1. Ambiguity in Thresholds and Categories
Challenge: As thresholds and exempt categories evolve, businesses may face difficulty in understanding whether they qualify for an exemption.
Solution: Keep track of the latest GST notifications and updates from the Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC). Ensure that your clients’ turnover and operational nature are reviewed regularly to assess compliance with the changing regulations.
2. e‑Invoice System Enablement vs Actual Requirement
Challenge: Some businesses are enabled on the e‑invoice portal but may not be required to issue e‑invoices due to exemption status.
Solution: Clarify to clients that being enabled on the portal does not automatically mean e‑invoice compliance is mandatory. Ensure clients file the exemption declaration to avoid non-compliance.
3. ITC Risks for Buyers
Challenge: Buyers may face issues claiming ITC if their supplier has failed to file the exemption declaration or issue an e‑invoice when required.
Solution: Educate clients (both suppliers and buyers) on the importance of exemption declarations and advise them to verify supplier compliance before processing ITC claims.
4. Integration with ERP Systems
Challenge: Ensuring that invoice templates in ERP systems are updated to reflect exemption status can be technically challenging for clients.
Solution: Work with your clients' IT teams to ensure that the invoice footer and exemption status are correctly incorporated into the system. Regular system updates will help ensure compliance is maintained automatically.
Stay Compliant with e‑Invoice Exemption Declaration Filing
As India moves towards full digitalisation of its tax system, compliance with the e‑invoice mandate and exemption declaration filing becomes increasingly important.
By understanding the exemption categories, properly filing the declaration on the e‑invoice portal, and maintaining the necessary documentation, you can help clients manage risk, preserve ITC, and stay audit-ready in this evolving tax landscape.
Stay proactive, stay informed, and ensure your clients are always ahead in the compliance game.
Similar Interesting Read: IMS Cycle in GST: How Invoice Management Works & Its Process
FAQs
Q1. What is the e‑invoice exemption under GST?
The e‑invoice exemption allows certain businesses to be exempt from the requirement of generating e‑invoices, even if their turnover exceeds the prescribed threshold. Exemptions are based on business type, such as banks, government bodies, transporters, and SEZ units.
Q2. How do I know if my client is exempt from e‑invoicing?
To determine exemption, check if your client falls under categories like banks, NBFCs, government entities, or transport agencies. Additionally, review the latest GST notifications to verify the client’s exemption eligibility.
Q3. How do I file the e‑invoice exemption declaration?
To file the exemption declaration, log into the e‑invoice portal (einvoice.gst.gov.in), navigate to the exemption declaration section, select the applicable exemption category, and submit the form using the authorized signatory’s DSC or EVC.
Q4. What happens if the exemption declaration is not filed?
Failure to file the exemption declaration can lead to audit risks, challenges in claiming ITC by buyers, and potential penalties for non-compliance with GST regulations.
Q5. Is it necessary to include an exemption statement on invoices?
Yes, businesses that are exempt from e‑invoicing should include a declaration on their invoices stating their exemption status, which helps buyers validate their eligibility to claim ITC.












