India's Goods and Services Tax regime has transformed how businesses manage their taxation and compliance requirements.
A critical element within the GST framework is the Invoice Management System (IMS), which plays a pivotal role in ensuring accurate tax reporting and smooth filing of returns.
For taxpayers in India, understanding the IMS cycle in GST is essential to maintain compliance, minimize errors, and streamline financial operations.
This blog provides a succinct overview of the IMS cycle, detailing key processes and practical insights into how invoice management works under GST.
TL;DR
- IMS cycle covers invoice creation, validation, submission, matching, and filing.
- Accurate invoice management ensures GST compliance.
- E-invoicing adds an IRN and a QR code for invoice verification.
- GST Automation tools simplify reconciliation and filing.
- Regular audits and GST updates prevent errors and penalties.
Understanding the IMS Cycle in GST
What is the IMS Cycle?
The Invoice Management System (IMS) in GST refers to the structured process of handling all invoice generation, validation, submission, and reconciliation aspects.
IMS integrates seamlessly with the GST portal, ensuring all invoices comply with GST rules and are correctly reflected in tax filings.
The IMS cycle is a backbone for invoicing accuracy, critical for compliance with GST laws and avoiding penalties.
Key Components of the IMS Cycle
- Invoice Generation: Creation of GST-compliant invoices with mandatory details.
- Invoice Validation: Checking invoices for accuracy and compliance before submission.
- Invoice Submission to GST Portal: Uploading e-invoices and receiving acknowledgement.
- Invoice Reconciliation and Matching: Aligning sales and purchase invoices to detect mismatches.
- Filing of GST Returns: Using accurate invoice data to file returns such as GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B.
Key Processes in the IMS Cycle
1. Invoice Generation and Documentation
Generating invoices that meet GST criteria is the first step in the IMS cycle. Every invoice must include:
- Supplier and recipient GSTIN
- Invoice number and date
- Description and quantity of goods/services
- Taxable value and rate of GST (CGST, SGST, IGST)
- Total amount including tax
Invoices under GST include tax invoices, debit and credit notes, receipt vouchers, and more, each with specific requirements.
2. Validation of Invoices
Before uploading invoices to the GST portal, it is crucial to validate each invoice to avoid errors that may lead to rejections or compliance issues. Common mistakes include mismatched GSTINs, incorrect taxable value, and invalid tax rates.
3. Invoice Submission and Reporting
With the implementation of e-invoicing for specified turnover thresholds, taxpayers must submit invoices electronically to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP).
An invoice reference number (IRN) and QR code are generated upon submission and must be mentioned on the physical and electronic invoice copies.
Timely and accurate submission enables real-time invoice tracking by the GST system and helps prevent fraudulent invoicing.
4. Reconciliation and Matching of Invoices
Matching sales invoices uploaded by suppliers with purchase invoices submitted by recipients is vital to reconciling tax credits and payments. Discrepancies in invoice data often cause disputes or delays in input tax credit claims.
Timely resolution of mismatches protects taxpayers from notices and penalties.
5. Return Filing Based on IMS Data
Accurate invoice data directly impacts the correctness of returns such as GSTR-1 (outward supplies) and GSTR-3B (summary returns). Efficient IMS practices simplify return filing, reduce revision needs, and speed up the refund process where applicable.
Practical Tips for Efficient Invoice Management
Leveraging Technology and Software Solutions
Automated, GST-compliant accounting and billing software are indispensable tools for managing invoices at scale. Features such as auto-generating e-invoices, error detection, and direct GST portal integration enhance accuracy and save time.
Suvit offers automated GST reconciliation and automated GST filing services. It streamlines the entire IMS cycle by automatically matching purchase and sales invoices, identifying discrepancies, and filing GST returns with minimal manual intervention.
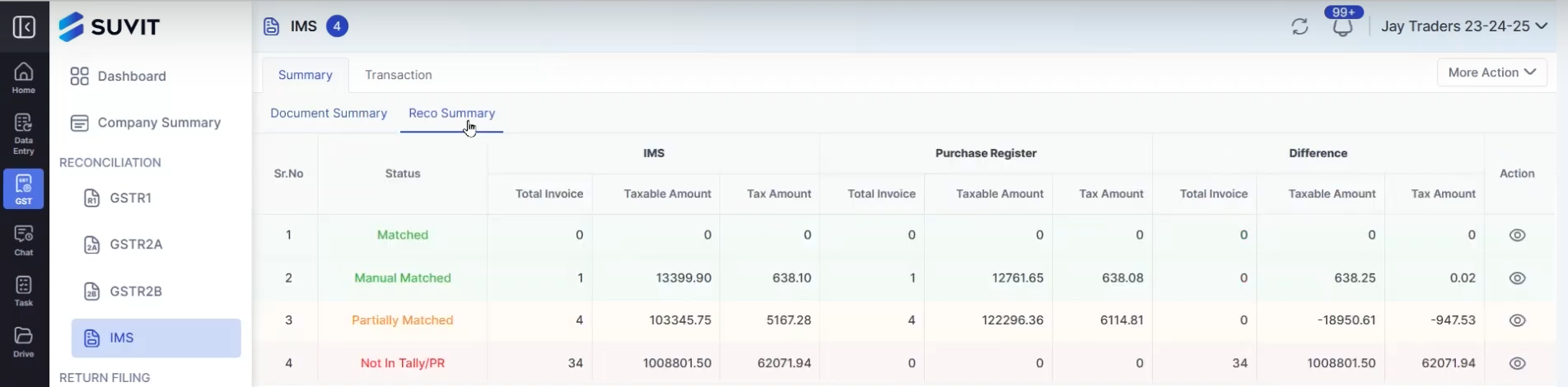
This reduces compliance risks, saves valuable time, and ensures timely GST submissions.
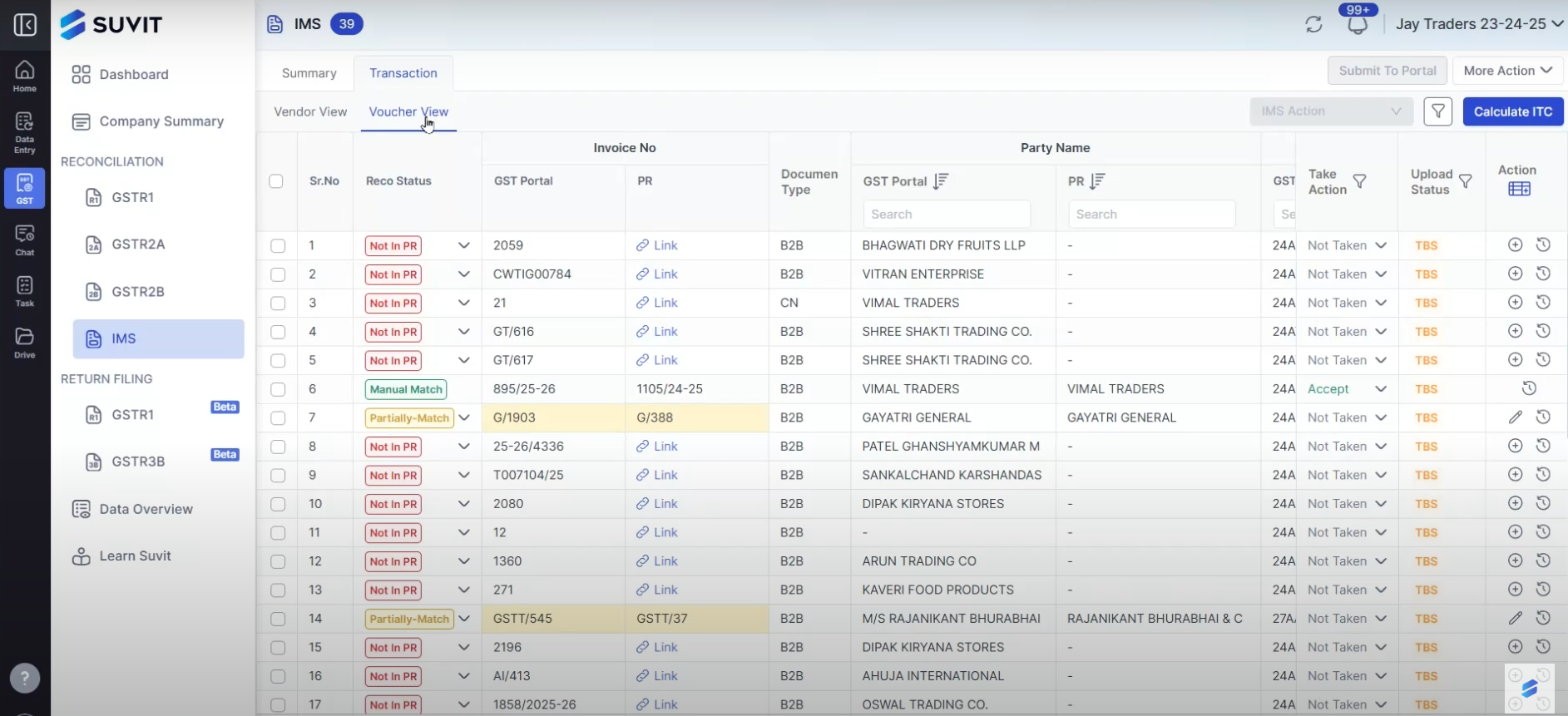
Look for systems that support real-time GST updates to keep your invoicing current with regulatory changes.
Ensuring Data Accuracy and Completeness
Regular audits of invoice data and cross-verification with trading partners help maintain data integrity. Any inconsistencies should be promptly addressed to prevent cascading errors during GST return filing.
Staying Updated with GST Amendments
The GST landscape evolves frequently with circulars and amendments related to invoice formats, thresholds, and e-invoicing mandates. Staying informed via official GST notifications and incorporating changes in IMS processes is key to ongoing compliance.
Handling Common Challenges in IMS
- Bulk invoice uploads: Use batch processing features in software solutions to manage large volumes effortlessly.
- Correcting errors in e-invoices: Amend mistakes promptly by issuing debit or credit notes as prescribed.
- Technical glitches on the GST portal: Maintain contingency plans and consider professional support for uninterrupted operations.
Strategic Importance of Effective IMS in GST Compliance
Efficient invoice management is vital for GST compliance and smooth business operations. By mastering the IMS cycle and leveraging automation, taxpayers can reduce errors, avoid penalties, and streamline filings. Staying accurate and updated ensures a hassle-free GST experience and supports transparent tax administration.
Try Suvit for free for a week!
FAQs
Q1: What is the IMS cycle in GST?
A1: The IMS cycle in GST refers to generating, validating, submitting, and reconciling invoices to ensure GST compliance and accurate return filing.
Q2: How does e-invoicing work under GST?
A2: E-invoicing involves electronically uploading invoices to the GST portal, where each invoice gets an Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and a QR code for authentication.
Q3: Why is invoice reconciliation meaningful in GST?
A3: Invoice reconciliation helps match sales and purchase invoices between suppliers and buyers, preventing mismatches that can block input tax credits or cause penalties.
Q4: Can software automate GST invoice management and filing?
A4: Yes, GST-compliant software like Suvit can automate invoice reconciliation and GST return filing, reducing errors and saving time.













