Welcome to our comprehensive guide on GSTR-1 – Return Filing, Format, Eligibility & Rules.
Understanding the GSTR-1 is essential for businesses to comply with GST regulations effectively and efficiently.
Let's delve into the essential aspects of this return filing process to ensure you are well-equipped for seamless compliance.
What is GSTR 1?
GSTR-1 is an important document in the GST system that captures details of all outward supplies or sales made by a registered taxpayer within a given tax period.
GSTR-1 is a form that needs to be filled out by every business registered under GST. However, there are some exceptions, which we'll talk about later. This form lists all the sales a business makes during a month or a quarter.
Now, GSTR-1 has a total of 13 sections, each with a specific purpose:
-
Tables 1, 2 & 3: Containing GSTIN, legal and trade names, and aggregate turnover in the previous year.
-
Table 4: Records taxable outward supplies to registered persons (including UIN-holders), excluding zero-rated supplies and deemed exports.
-
Table 5: Records taxable outward inter-state supplies to unregistered persons where the invoice value exceeds Rs. 2.5 lakh.
-
Table 6: Accounts for zero-rated supplies and deemed exports.
-
Table 7: Records taxable supplies to unregistered persons not covered in Table 5 (net of debit notes and credit notes).
-
Table 8: Lists outward supplies that are Zero-rated, exempted, or non-GST in nature.
-
Table 9: Documents amendments to taxable outward supplies reported in Tables 4, 5 & 6 of previous tax periods' GSTR-1 return (including debit notes, credit notes, and refund vouchers issued during the current period).
-
Table 10: Records debit notes and credit notes issued to unregistered persons.
-
Table 11: Information about advances received, adjusted for in the current tax year, or changes to data reported in the previous tax year.
-
Table 12: Summarizes outward supplies based on HSN codes.
-
Table 13: Lists documents issued during the period.
-
Table 14: For suppliers - Reports ECO operators' GSTIN-wise sales through e-commerce operators, subject to TCS collection under section 52 or tax payment under section 9(5) of the CGST Act.
-
Table 14A: For suppliers - Documents amendments to Table 14.
-
Table 15: For e-commerce operators - Reports both B2B and B2C, suppliers' GSTIN-wise sales through e-commerce operators, on which e-commerce operators must deposit TCS under section 9(5) of the CGST Act.
-
Table 15A: For e-commerce operators -
- Table 15A I: Documents amendments to Table 15 for sales to GST registered persons (B2B).
- Table 15A II: Documents amendments to Table 15 for sales to unregistered persons (B2C).
So, that's basically what GSTR-1 is all about—it's a detailed record of a business's sales for a specific period, and it's essential for staying compliant with GST regulations.
When is the GSTR-1 Deadline?
The GSTR-1 deadlines are determined by your total turnover. Under the QRMP scheme, businesses with sales up to Rs. 5 crore can file quarterly returns, which are due by the 13th of the month that follows the relevant quarter.
On the other hand, taxpayers who choose not to participate in the QRMP scheme or whose monthly revenue exceeds Rs. 5 crore are required to submit their returns by the 11th of the following month.
Watch a Video: GST Reconciliation through VYAPAR TAXONE
Who Needs to File GSTR-1?
Whether or not there are any transactions during the period, each registered person must file a GSTR-1.
There is an option to file through an SMS for those who file a zero GSTR-1, and it went live in the first week of July 2020. The following individuals are exempt from filing GSTR-1:
- Distributors of Input Services Dealers of Composition
- Providers of online information and database access or retrieval services (OIDAR), who are required by Section 14 of the IGST Act to pay tax on their own
- Taxable person who is not a resident
- Taxpayer liable to collect TCS
- Taxpayer liable to deduct TDS
Late Fees and Penalty for GSTR-1 Filing
-
CGST Act, 2017
- Late fees for every day of delay: Rs 25
- Maximum late fee for turnover up to Rs.1.5 crore: Rs 1,000
- Maximum late fee for turnover between Rs.1.5 crore and Rs.5 crore: Rs 2,500
- Maximum late fee for turnover more than Rs.5 crore: Rs 5,000
-
Respective SGCT Act, 2017 / UTGST Act, 2017
- Late fees for every day of delay: Rs 25
- Maximum late fee for turnover up to Rs.1.5 crore: Rs 1,000
- Maximum late fee for turnover between Rs.1.5 crore and Rs.5 crore: Rs 2,500
- Maximum late fee for turnover more than Rs.5 crore: Rs 5,000
-
Total Late Fees to be Paid
- For every day of delay: 50
- For turnover up to Rs.1.5 crore: Rs 2,000
- For turnover between Rs.1.5 crore and Rs.5 crore: Rs 5,000
- For turnover more than Rs.5 crore: Rs 10,000
Also Read: Sync Your Excel Data with Tally in Minutes Using VYAPAR TAXONE
The following information outlines the late fee applicable for nil GSTR-1 filings.
-
CGST Act, 2017
- Late fees for every day of delay: Rs 10
- Maximum late fee: Rs 250
-
Respective SGCT Act, 2017 / UTGST Act, 2017
- Late fees for every day of delay: Rs 10
- Maximum late fee: Rs 250
-
Total Late Fees to be Paid
-
For every day of delay: Rs 20
-
Maximum late fee: Rs 500
-
Also Read: A Guide to GSTR 2A, GSTR 2B, and GSTR 3B for GST Compliance
How to Reconcile GSTR-1 Using Vyapar TaxOne?
Vyapar TaxOne provides the GST Audit feature, enabling users to review the due dates for filing GSTR1, GSTR 2A, and GSTR 3B returns, and download the corresponding PDF files.
Here you can see how easy it is to reconcile GSTR 1 with Vyapar TaxOne:
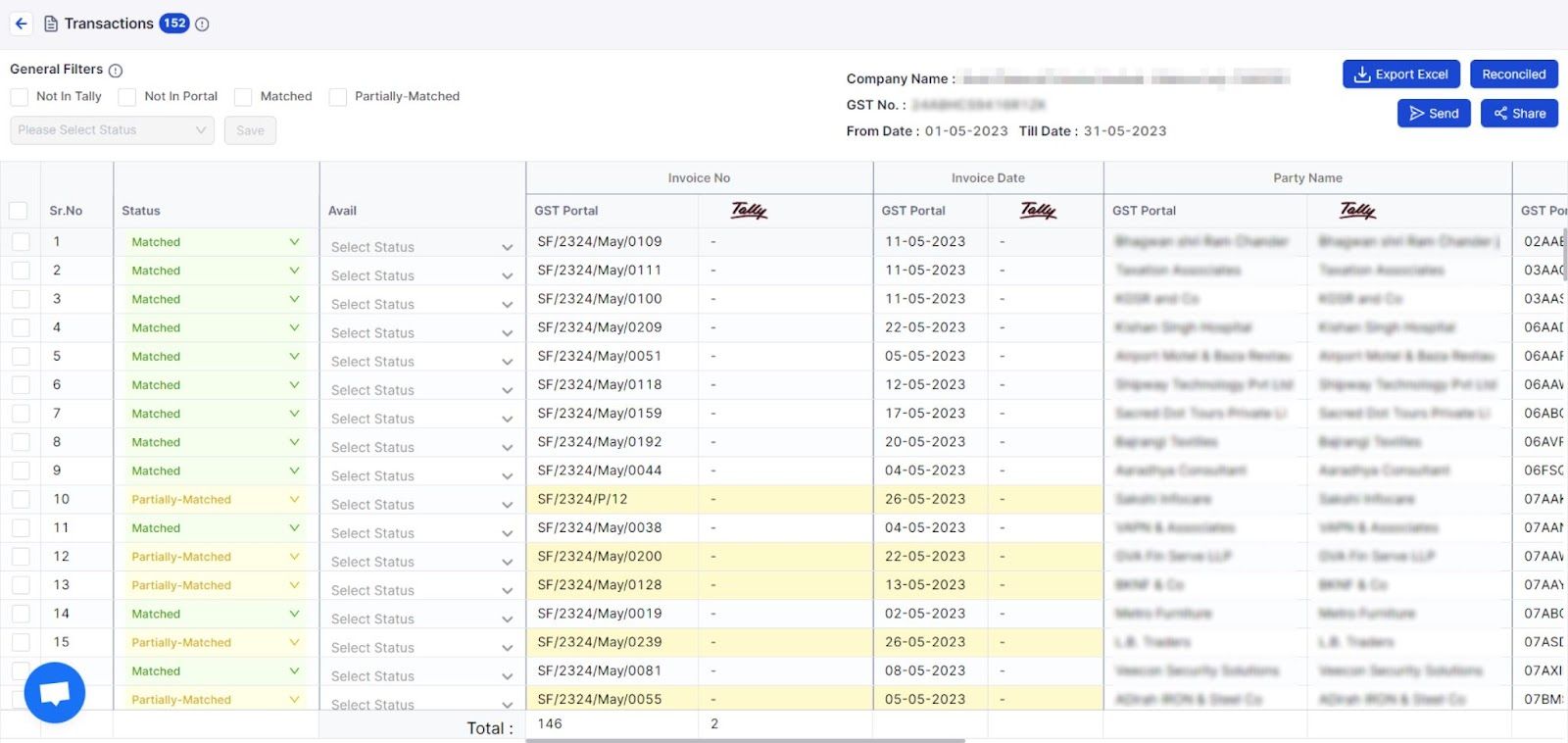
You will get 4 types of status results for your data. You can fetch your data from GST portal and directly match it with Tally data from Vyapar TaxOne.
You can also check the eligibility of specific HSNs in the Input Tax Credit (ITC) based on whether they are eligible, ineligible, blocked, or exempt.
So why delay? Start with our seven day free trial from here!
FAQS on GSTR 1?
1. Can I modify the invoices uploaded on the GST portal?
Yes, you can make changes to uploaded invoices multiple times before submitting a return. However, once a return is submitted, the numbers are frozen, and changes cannot be made.
2. Do I need to file GSTR-1 if there are no sales in a month?
Yes, filing GSTR-1 is mandatory even if there were no sales during a month/quarter. You need to file Nil GSTR-1 in such cases.
3. Can I file GSTR-1 after the due date?
Yes, you can file GSTR-1 after the due date, but a late fee will be charged based on the number of delayed days.
4. What's the difference between GSTR-1 & GSTR-3B?
GSTR-1 requires reporting detailed sales information, while GSTR-3B summarizes sales, Input Tax Credit (ITC) claimed, and net tax payable
5. Do I need to make a GST payment after filing GSTR-1?
No, GSTR-1 is for reporting sales details to the government. You need to pay the tax due while filing GSTR-3B.












