When it comes to GST filing, GSTR 1 Reconciliation is one of the most important steps for businesses to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
Accurate reconciliation helps businesses stay in line with legal requirements and facilitates the smooth functioning of the GST system.
This step-by-step guide will walk you through the entire process of GSTR 1 reconciliation, provide actionable insights, and explain how using automation tools like Vyapar TaxOne can help simplify the task.
What is GSTR 1?
GSTR 1 is a monthly or quarterly GST return that businesses must file with the GST portal. This return includes details of outward supplies, such as sales invoices, debit notes, credit notes, exports, and other transactions. Filing GSTR 1 is essential to ensure that the GST paid on sales is accurately reported and matched with the buyer’s GST returns (GSTR 2A).
While filing GSTR 1 is mandatory for businesses with a turnover exceeding Rs 5 crores, smaller businesses with a turnover below Rs 5 crores may file quarterly returns.
Why is GSTR 1 Reconciliation Important?
Reconciliation of GSTR 1 ensures that the data reported in your return matches the details submitted by your recipients in their GSTR 2A (purchase return). This helps maintain data integrity, avoiding discrepancies and ensuring no mismatches between the sales and purchase records.
Here’s why reconciliation matters:
- Avoid Penalties: Incorrect or delayed filing can lead to penalties.
- Maintain Compliance: Proper reconciliation ensures you're adhering to GST guidelines and prevents audit risks.
- Smooth Processing of Refunds: Accurate data ensures timely input tax credits and refunds processing.
Understanding the Basics of GSTR 1
Before diving into the reconciliation process, let’s cover some basics.
What Information is Included in GSTR 1?
GSTR 1 includes:
- Sales Invoices: A complete record of goods and services sold and GST details.
- Debit/Credit Notes: Adjustments for returns or discounts.
- Exports: Information about goods and services exported outside India.
- Advance Payments: Any advance payments received before delivery.
- HSN/SAC Codes: Required for categorizing goods and services.
Filing Frequency and Deadlines
- Monthly Filing: Businesses with a turnover exceeding Rs 5 crores must file GSTR 1 monthly.
- Quarterly Filing: Smaller businesses with a turnover of less than Rs 5 crores may opt for quarterly filing.
Common Mistakes in GSTR 1 Filing
- Incorrect HSN/SAC codes.
- Wrong GST rates applied.
- Mismatched customer details.
- Failing to report export supplies or advances.
What is GSTR 1 Reconciliation?
GSTR 1 reconciliation involves comparing your filed GSTR 1 data with the information in your recipient’s GSTR 2A (the buyer’s purchase return). The goal is to ensure that:
- All sales invoices in GSTR 1 match the buyer’s details in GSTR 2A.
- There are no discrepancies between the reported tax amounts.
- All transactions are properly categorized.
Why is GSTR 1 Reconciliation Vital?
- Avoid Discrepancies: Mismatched data can lead to rejection of your return or penalties.
- Accurate Credit Claims: Ensures your input tax credit claims are valid.
- Improved Audit Compliance: Reduces the chances of discrepancies during an audit.
Key Steps for GSTR 1 Reconciliation
Now, let's break down the process of GSTR 1 Reconciliation in a step-by-step manner.
Step 1: Gather the Required Documents
Start by gathering all the necessary documents for reconciliation:
- Sales Invoices: Ensure that all invoices are correctly recorded.
- Purchase Records: Match the sales records with purchase records.
- Debit/Credit Notes: Include adjustments for returns or discounts.
- Export Documents: If applicable, include details of exported goods/services.
Step 2: Cross-check the Sales Invoices
Ensure that the sales invoices entered in GSTR 1 match the invoices issued to customers. This includes:
- Correct HSN/SAC Codes.
- Accurate GST Rates.
- Customer details (name, GSTIN, etc.).
Make sure that no transactions are missed, especially for export supplies, as these require zero-rated GST.
Step 3: Match Data with GSTR 2A
The next step is to compare the data in GSTR 1 with the buyer’s GSTR 2A. The buyer’s GST return should reflect your sale, as GSTR 2A automatically picks up sales made to the buyer.
- Ensure tax amounts match.
- Ensure invoice details (such as GSTIN) are correct.
- Look for any mismatched entries and make necessary corrections.
Step 4: Correct Errors or Discrepancies
If you find any discrepancies, you can rectify them in your next GSTR 1 filing. Common methods to correct errors include:
- Issuing Credit/Debit Notes: For returned goods or price adjustments.
- Amendment of Sales Invoices: For errors in GST rates or invoice details.
Step 5: Use GST Reconciliation Software or Tools
Using software tools can simplify the reconciliation process. Popular options include Tally, Zoho Books, and Vyapar TaxOne. These tools allow you to:
- Automate Data Collection: Sync your sales data directly with GST filings.
- Detect Errors: Automatically identify discrepancies between GSTR 1 and GSTR 2A.
- Streamline the Filing Process: Simplify data entry and filing.
Common Challenges in GSTR 1 Reconciliation
Mismatched Taxable Values
Sometimes, the taxable values reported in GSTR 1 may not match GSTR 2A due to discrepancies in invoice entries. To resolve this, ensure both parties have accurate records and update invoices as necessary.
Unmatched Invoices or Missing Entries
Missing or unreported invoices are a common problem. Double-check all transactions and ensure every sale is accounted for in GSTR 1.
Late Reporting
Late reporting of transactions can lead to mismatches between your GSTR 1 and GSTR 2A. Always ensure timely reporting of all invoices and payments.
Handling Sales Returns and Adjustments
Sales returns and adjustments should be carefully managed in your GSTR 1 filings. Use credit notes or adjustments to update the records accordingly.
Best Practices for Effective GSTR 1 Reconciliation
Regular and Timely Updates
Ensure that your sales records are updated regularly to avoid last-minute errors. This also helps to ensure the data is always up-to-date.
Automation for Efficiency
Automating your GSTR 1 reconciliation using software like Vyapar TaxOne will save you time and reduce human errors. Automation ensures data accuracy and timely filing.
Audit Trail and Documentation
Maintain detailed records of all reconciled entries, including amendments and adjustments. This will help during audits and give you a complete trail of your filings.
Collaborating with Tax Professionals
It’s always helpful to consult with GST professionals or consultants for complex reconciliations. Their expertise can help resolve any challenging discrepancies and ensure compliance.
How Vyapar TaxOne Helps in GSTR 1 Reconciliation
Vyapar TaxOne is an advanced GST reconciliation tool that simplifies the GSTR 1 filing and reconciliation process. Here’s how it can assist:
- Automated Data Collection:
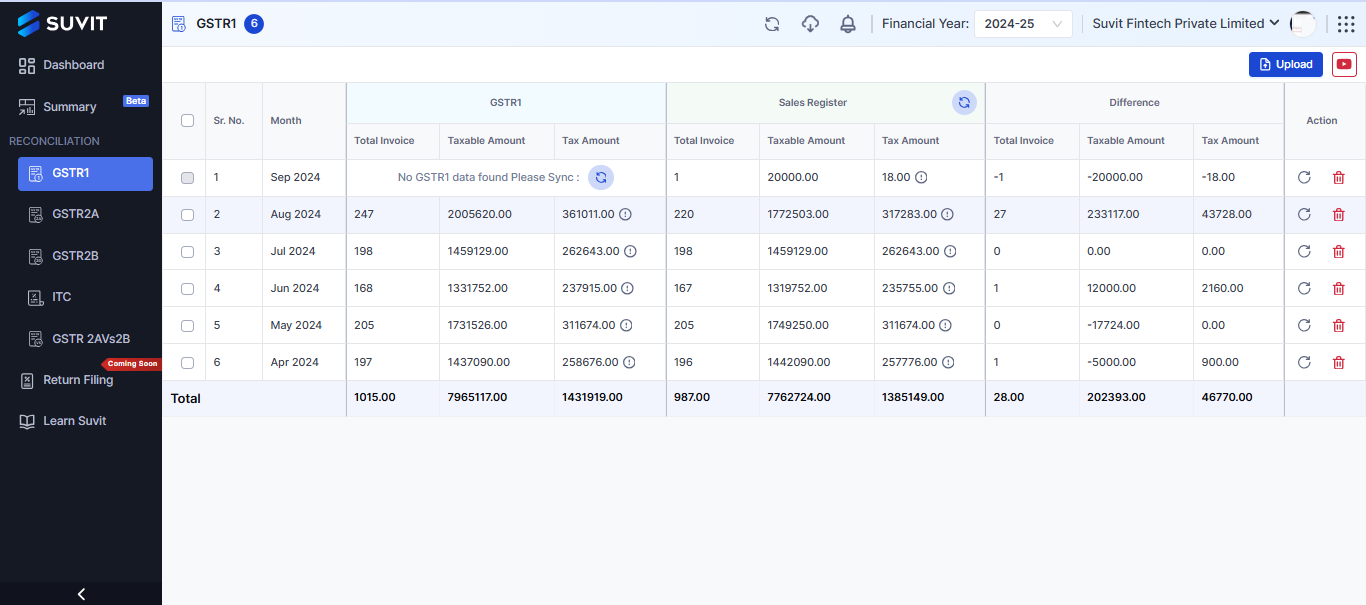
Vyapar TaxOne automatically collects and compiles data from your accounting software, minimizing manual errors.
- Real-Time Syncing:
It syncs data with the GSTN portal in real time, ensuring that all your details are accurate and up-to-date.
- Error Detection:
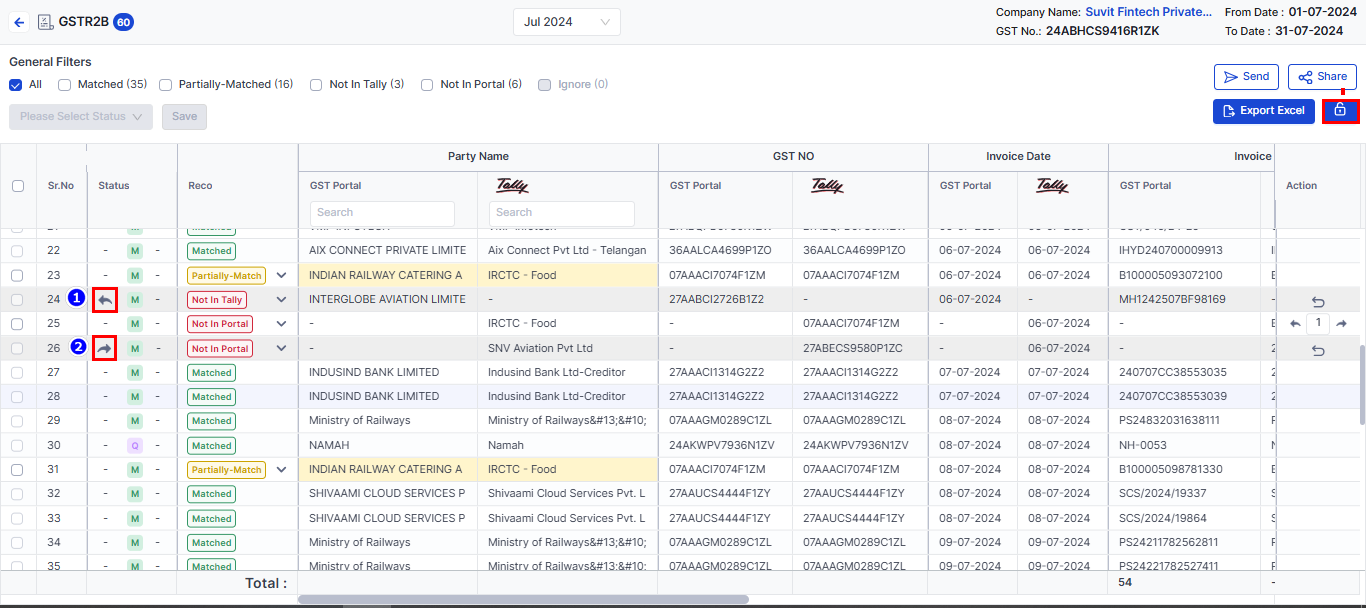
Vyapar TaxOne identifies discrepancies between your GSTR 1 and the recipient’s GSTR 2A and provides statuses like Not in Tally, Partially-Match and Matched.
- Simplified Filing:
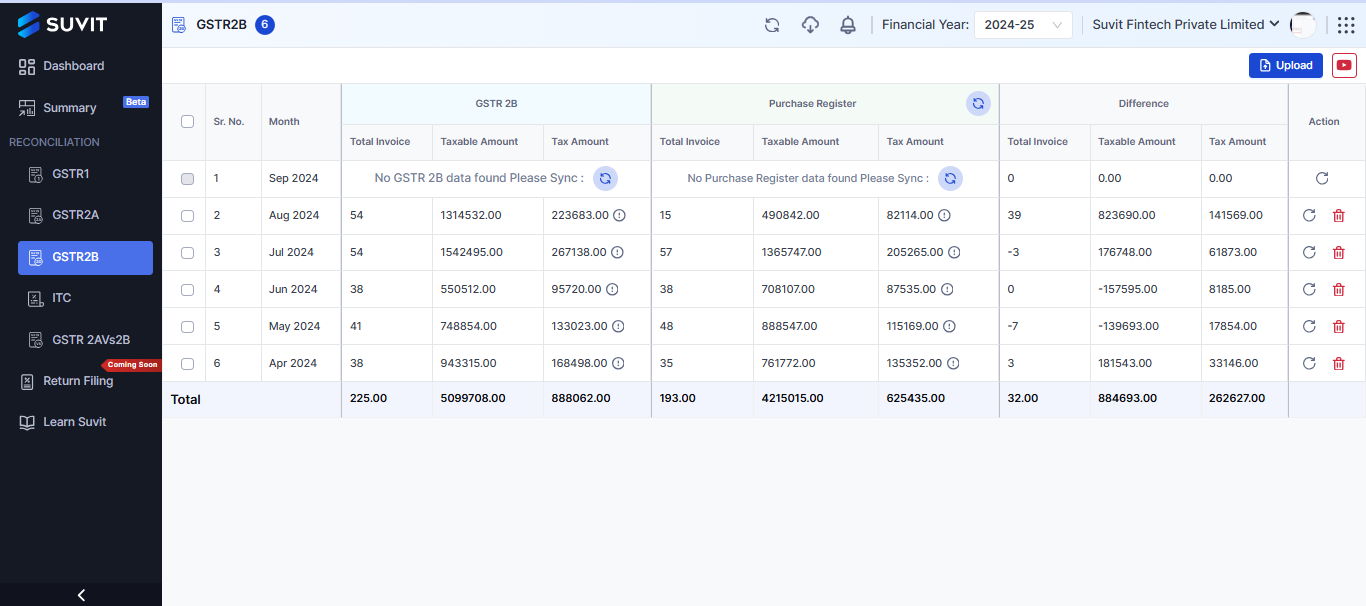
With an intuitive interface, Vyapar TaxOne helps you easily review, amend, and reconcile GSTR 1.
- Reports and Insights:
Vyapar TaxOne generates reports that offer insights into your sales, taxes, and compliance status.
You can get complete details here!
Consequences of Incorrect GSTR 1 Reconciliation
GST Audits and Penalties
Incorrect reconciliation can lead to audits by tax authorities and the imposition of penalties. Timely and accurate reconciliation helps you avoid such complications.
Impact on GST Returns and Refunds
Incorrect data can affect your GST returns and refunds. Discrepancies in GSTR 1 can cause delays in claiming input tax credits or receiving refunds.
TL;DR
GSTR 1 Reconciliation matches the details in your GSTR 1 (outward supplies) with the data in GSTR 2A (purchases) submitted by your recipients. This ensures data accuracy and compliance and prevents discrepancies.
Steps include gathering documents, cross-checking invoices, matching data with GSTR 2A, correcting errors, and using tools like Vyapar TaxOne to automate the process. Regular reconciliation can help businesses avoid penalties, ensure timely refunds, and maintain smooth GST operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is GSTR 1 reconciliation?
GSTR 1 reconciliation ensures that the details of your sales and outward supplies reported in GSTR 1 match with the corresponding information in the recipient’s GSTR 2A (purchase return). This helps to avoid discrepancies and penalties and ensure compliance with GST regulations.
2. Why is GSTR 1 reconciliation necessary?
Reconciliation ensures that the sales data in your GSTR 1 is accurate and consistent with the purchase details reported by your recipients. It helps maintain the integrity of the GST filing process and prevents mismatches that could result in penalties or audit scrutiny.
3. What are common issues faced during GSTR 1 reconciliation?
Common issues include mismatched tax amounts, missing invoices, incorrect HSN/SAC codes, and discrepancies in customer details (such as GSTIN). These issues can lead to incorrect filings and delays in refunds or input tax credit claims.
5. What are the consequences of incorrect GSTR 1 reconciliation?
Incorrect reconciliation can lead to penalties, audit notices, and delays in receiving input tax credits or refunds. Mismatched data can also cause discrepancies in the recipient’s records, leading to complications in the overall GST process.
6. Can I reconcile GSTR 1 manually?
Yes, GSTR 1 reconciliation can be done manually by comparing the details in GSTR 1 with GSTR 2A. However, this can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Tools like Vyapar TaxOne can automate the process, reducing the risk of mistakes and saving time.













